Last summer, while sitting in my garden, my 14-year-old Chihuahua, Luna, trotted up beside me with her favorite squeaky toy, the same one she’s had since she was a puppy. Watching her tiny paws shuffle across the grass reminded me how time gently shapes our pets’ lives.
Luna wasn’t as quick as she used to be, but her spark was still there, her bright eyes, her playful bark, her insistence on sitting in my lap while I worked.
That moment made me reflect on how Chihuahuas, despite their small size, often live long, fulfilling lives filled with personality and devotion. They can outlive many other breeds, thanks to their sturdy genetics and strong spirit.
Understanding the Chihuahua lifespan average helps owners like me make the most of every stage from the energetic puppy days to the gentle, slow-paced senior years. Whether you have a short-haired or long-haired Chihuahua, their lifespan depends on nutrition, environment, and how much love and care you provide along the way.
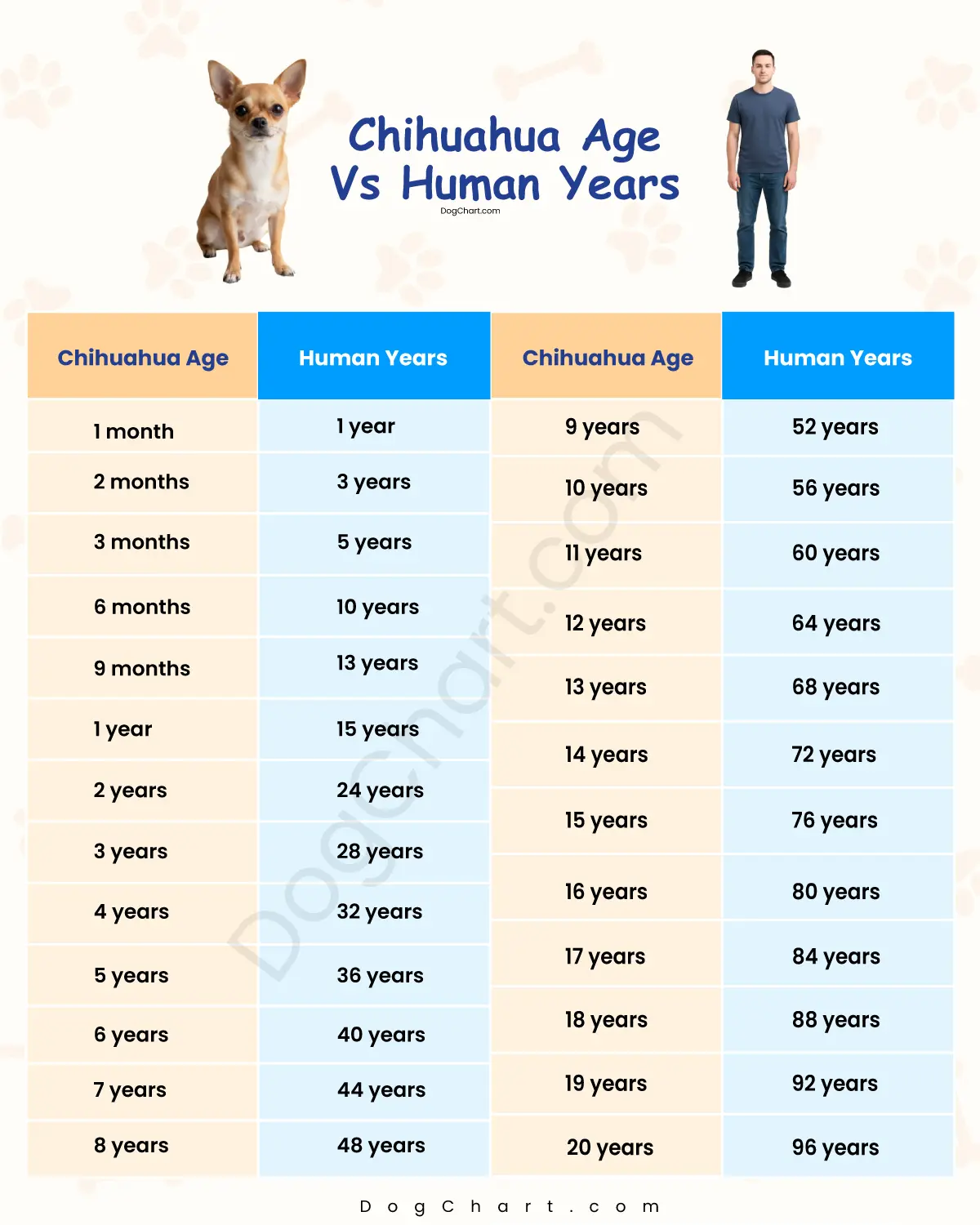
Table of Contents
How Chihuahua Aging Differs from Other Dog Breeds
Chihuahuas age differently due to their tiny size and slow internal wear-and-tear rate, which gives them an impressively long lifespan. While large dogs may be considered seniors by age six or seven, a Chihuahua often remains lively and youthful well into its teens.
Unlike bigger breeds, their bones, joints, and organs face less strain over time. However, aging in Chihuahuas manifests through subtler signs, such as slight dental wear, thinning fur, or lower stamina, rather than major physical changes seen in large breeds.
It’s important to understand that one Chihuahua year doesn’t always equal seven human years. Smaller dogs have a more gradual aging curve, especially after age five.
Providing balanced nutrition, gentle daily walks, and mental stimulation (like short training games) can help slow their biological aging process. Regular vet checkups also ensure early detection of any health changes that might affect longevity and comfort.
Chihuahua’s Life Stage
Each chihuahua age in human years brings different nutritional, emotional, and health requirements. Recognizing which stage your dog is in helps tailor care to their specific needs, from playful puppyhood to wise senior years.
| Chihuahua Age | Human Years | Life Stage |
| 1 month | 1 year | Newborn |
| 2 months | 3 years | Puppy |
| 3 months | 5 years | Puppy |
| 6 months | 10 years | Juvenile |
| 9 months | 13 years | Adolescent |
| 1 year | 15 years | Young Adult |
| 2 years | 24 years | Adult |
| 3 years | 28 years | Adult |
| 4 years | 32 years | Adult |
| 5 years | 36 years | Mature Adult |
| 6 years | 40 years | Mature Adult |
| 7 years | 44 years | Senior |
| 8 years | 48 years | Senior |
| 9 years | 52 years | Senior |
| 10 years | 56 years | Senior |
| 11 years | 60 years | Senior |
| 12 years | 64 years | Senior |
| 13 years | 68 years | Senior |
| 14 years | 72 years | Senior |
| 15 years | 76 years | Elderly |
| 16 years | 80 years | Elderly |
| 17 years | 84 years | Elderly |
| 18 years | 88 years | Elderly |
| 19 years | 92 years | Elderly |
| 20 years | 96 years | Elderly |
Puppy Stage
In the puppy phase, Chihuahuas grow rapidly both mentally and physically. This stage typically lasts from birth to 6–8 months. During this time, proper diet, socialization, and basic obedience training are key. Puppies also require extra warmth, gentle handling, and consistent routines to build confidence.
| Puppy Age | Equivalent Human Years | Feeding Frequency | Training Focus | Activity Level |
| 2 months | 1 year | 4–5 times daily | Crate & potty training | Very high |
| 4 months | 3 years | 4 times daily | Socialization & name recall | High |
| 6 months | 5 years | 3 times daily | Basic obedience | Moderate |
| 8 months | 7 years | 2–3 times daily | Leash walking | Moderate |
Young Adult Stage
The young adult stage (approximately 8 months to 3 years) is when Chihuahuas are full of energy and curiosity. They develop stronger bonds with their owners and benefit from consistent routines.
Regular exercise and a high-protein diet are essential to support their metabolism and muscle tone. This is also the period to establish long-term healthy habits, including dental care and portion-controlled meals.
| Dog Age | Equivalent Human Years | Energy Level | Recommended Exercise | Health Focus |
| 1 year | 10–12 years | Very high | 30–45 min daily | Bone growth |
| 2 years | 20–24 years | High | 45–60 min daily | Weight management |
| 3 years | 28 years | Moderate | 30–40 min daily | Dental care |
Adult Stage
Between ages 3 and 8, your Chihuahua enters adulthood. This is when energy levels balance, and your dog is at its peak health. A well-balanced diet, portion control, and regular vet visits are critical during this stage. Though they may appear mature, they still thrive on attention and interactive play. Owners should begin monitoring their weight and joints more closely, as metabolism begins to slow.
| Dog Age | Equivalent Human Years | Energy Level | Diet Needs | Vet Visits |
| 4 years | 32 years | Moderate | Balanced food portions | Once yearly |
| 5 years | 36 years | Moderate | Weight maintenance | Yearly checkup |
| 6 years | 40 years | Slightly lower | Heart-healthy diet | Every 6 months |
| 8 years | 48 years | Mild decline | Senior diet | Every 6 months |
Senior Stage
The senior stage starts around age 9 and continues through the rest of the dog’s lifespan. At this point, Chihuahuas slow down physically and may develop age-related issues such as arthritis or dental disease.
A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3s, and soft-textured Chihuahua food is ideal for maintaining vitality. Gentle walks, mental enrichment, and regular grooming keep them happy and engaged.
| Dog Age | Equivalent Human Years | Energy Level | Special Care Needs | Common Health Focus |
| 9 years | 52–55 years | Moderate | Softer food, more rest | Dental & heart health |
| 11 years | 60–65 years | Low | Joint supplements | Mobility issues |
| 13 years | 70–75 years | Low | Extra warmth, short walks | Vision/hearing |
| 15+ years | 80–90 years | Very low | Comfort care | Overall well-being |
Factors That Affect a Chihuahua’s Aging Process
Several key factors influence how quickly or slowly a Chihuahua ages, from genetics and environment to diet and lifestyle. Genetics play one of the biggest roles; some bloodlines naturally live longer due to stronger immune systems and lower predisposition to diseases.
Proper nutrition is another critical element, feeding your Chihuahua balanced, high-quality food throughout their life supports bone strength, heart health, and metabolism.
Exercise and mental stimulation also affect aging. Chihuahuas that stay active, even through light play or short walks, maintain better muscle tone and mental sharpness as they age.
Environmental factors, such as living indoors in a calm, loving home, can slow down aging compared to dogs that face chronic stress or neglect. Lastly, routine vet checkups and preventive care, including dental cleanings and vaccinations, can significantly extend the Chihuahua’s lifespan by catching problems early before they worsen.
Signs Your Chihuahua Is Getting Older
As your Chihuahua enters their senior years, you’ll notice subtle but distinct changes in their behavior, body, and energy. Older dogs tend to slow down, rest more often, and show less interest in long play sessions.
You may also spot physical changes like a graying muzzle, cloudiness in the eyes, or stiffness after waking up. Here are some quick indicators to watch for:
- Slower movement
- Reduced appetite
- Increased sleep
- Dental issues
- Cloudy eyes
- Weight changes
- Less social engagement
How to Care for an Aging Chihuahua
Caring for a senior Chihuahua means adapting to their new needs with patience and consistency. Comfort and health become top priorities during this stage. Soft bedding, a warm sleeping space, and easy access to food and water make daily life easier. Dental care should remain consistent since older dogs are more prone to tooth decay and gum disease.
Regular veterinary checkups, ideally every six months, help monitor for age-related issues such as arthritis, heart murmurs, or weight gain. Gentle daily walks keep joints flexible without overexertion. Emotional support also plays a big role; elderly Chihuahuas thrive on affection and stability, so maintaining familiar routines reduces anxiety and confusion.
Diet and Exercise Tips for Senior Chihuahuas
Diet and activity become increasingly important as your Chihuahua ages. Switching to senior-specific food ensures they receive fewer calories but more fiber, antioxidants, and joint-supporting nutrients. Avoid feeding table scraps, as aging digestive systems are more sensitive to fatty or processed foods. To keep them active and engaged:
- Short daily walks
- Gentle indoor play
- Mental puzzles
- Soft chew toys
- Stretching time
Common Health Problems in Older Chihuahuas
Like all small breeds, older Chihuahuas are prone to specific health conditions that can affect their comfort and mobility. Regular monitoring, early detection, and proper diet are crucial for managing these issues effectively.
| Health Problem | Common Symptoms | Prevention | Treatment | Severity |
| Dental Disease | Bad breath, tooth loss | Regular brushing | Vet cleaning | Moderate |
| Arthritis | Stiffness, limping | Gentle exercise | Joint supplements | Moderate |
| Heart Disease | Fatigue, coughing | Healthy diet | Medication | High |
| Obesity | Weight gain | Portion control | Low-calorie food | High |
| Vision Loss | Cloudy eyes | Vet eye exams | Eye drops/surgery | Moderate |
Lifespan of a Chihuahua Compared to Other Small Breeds
Chihuahuas are among the longest-living dog breeds, with an average lifespan of 12–20 years depending on genetics, diet, and overall care. When compared to other small breeds, Chihuahuas often outlive their counterparts, thanks to their slow metabolism and light body structure. Maintaining a consistent diet and regular exercise plays a major role in their longevity.
| Breed | Average Lifespan | Common Health Issues | Energy Level | Diet Type |
| Chihuahua | 12–20 years | Dental, heart issues | Moderate | Balanced food |
| Pomeranian | 12–16 years | Collapsing trachea | High | Protein-rich diet |
| Maltese | 12–15 years | Skin allergies | Moderate | Hypoallergenic food |
| Shih Tzu | 11–16 years | Eye infections | Low | Low-fat diet |
| Yorkshire Terrier | 13–17 years | Dental issues | Moderate | Grain-free diet |
How to Keep Your Chihuahua Healthy for Longer
The secret to a long and vibrant Chihuahua lifespan lies in proactive, loving care. Prioritize a well-balanced diet, daily activity, and mental engagement. Keep them mentally stimulated with short training sessions or scent games, which delay cognitive decline.
Make regular vet checkups non-negotiable, even if your dog seems perfectly fine. Early detection of conditions like heart murmurs or joint pain can add years to their life. Above all, emotional well-being is just as vital as physical health. Give them affection, stability, and comfort, and your Chihuahua will reward you with loyalty and love for years beyond the average.
FAQs
What is the average lifespan of a Chihuahua?
Most Chihuahuas live between 12 and 20 years, depending on genetics, diet, and care quality.
How can I help my Chihuahua live longer?
Feed balanced food, ensure regular vet visits, and keep them active daily.
Do long-haired Chihuahuas live longer than short-haired ones?
Their lifespan is generally the same; care and genetics matter more than coat type.
When is a Chihuahua considered a senior dog?
Around 8–9 years old, though some may not show age-related signs until 10 or 11.
What’s the oldest recorded Chihuahua age?
Some have lived up to 23 years with excellent care and a loving environment.